Sovereign AI: Building National Control Over Artificial Intelligence
Sovereign AI refers to the strategic initiative by countries or regions to develop and manage artificial intelligence (AI) systems independently of dominant foreign tech platforms—particularly those outside the European Union. This approach emphasizes national control over AI technologies to ensure alignment with local values, reduce reliance on external providers, and maintain oversight of critical infrastructure. Two core pillars define sovereign AI: control over the algorithms and data used to train AI models, and sovereignty over the infrastructure where AI systems operate.
Strategic Autonomy and National Security
Nations are increasingly prioritizing the development of AI systems that are free from foreign influence, especially in sectors vital to national security, critical infrastructure, and economic resilience. Sovereign AI supports strategic autonomy by reducing exposure to potentially biased or insecure foreign-developed AI technologies.
Cultural and Ethical Alignment
AI systems developed within a sovereign framework are tailored to reflect local languages, cultural norms, and ethical standards. This ensures that AI-driven decisions are contextually appropriate and reduces the risk of cultural misalignment, bias, or discrimination.
Data Sovereignty and Privacy Protection
Data is the foundation of AI development. Sovereign AI initiatives emphasize keeping data within national borders to ensure compliance with local privacy laws, safeguard sensitive information, and prevent the extraterritorial application of foreign regulations.
Driving Economic Growth and Innovation
By fostering domestic AI capabilities, countries can stimulate innovation, protect intellectual property, and enhance competitiveness in the global tech landscape. Sovereign AI enables nations to lead in emerging technologies while creating new economic opportunities.
Ethical AI and Governance
Governments are increasingly focused on ensuring that AI systems are transparent, accountable, and aligned with human rights and national laws. Sovereign AI frameworks prioritize ethical governance to mitigate risks such as economic displacement, privacy violations, and unfair decision-making.
Key EU Regulations Supporting Sovereign AI
EU AI Act
Set to be fully enforced in 2025, the EU AI Act is a pioneering regulatory framework that classifies AI systems based on risk levels—from low to high. High-risk applications, such as those in healthcare or law enforcement, must meet strict requirements for safety, transparency, and accountability. Key provisions include:
– Mandatory testing and certification for high-risk AI systems.
– Transparency obligations to explain AI decision-making.
– Clear accountability structures for AI-related harms.
EU Data Act
Effective from 2023, the EU Data Act enhances data accessibility and governance. It promotes fair data sharing, enables switching between cloud providers, and supports AI development by improving access to training data. This regulation is crucial for reducing vendor lock-in and fostering innovation within national jurisdictions.
NIS2 Directive (Cybersecurity Act)
The NIS2 Directive strengthens cybersecurity across EU member states, particularly in critical sectors like energy, transport, and digital services. It mandates robust cybersecurity practices and incident reporting, ensuring that AI systems used in essential infrastructure are secure and resilient.
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
DORA focuses on operational resilience and cybersecurity in the financial sector. It sets stringent requirements for risk management, performance monitoring, and supply chain transparency. As AI becomes integral to financial services, DORA ensures these systems are protected from cyber threats and operational disruptions.
Challenges to Achieving Sovereign AI
Infrastructure and Resource Limitations
Developing sovereign AI requires substantial investment in computing infrastructure, data centers, and energy resources. Many countries face difficulties in acquiring the necessary hardware—such as high-performance GPUs—and energy capacity to support large-scale AI operations.
Talent Shortages
AI development demands specialized expertise in data science, machine learning, and engineering. Nations must invest in education and training to build a skilled workforce capable of supporting sovereign AI initiatives.
Global Interdependence
Despite the push for sovereignty, AI development often relies on international collaboration and data sharing. Countries must strike a balance between maintaining control and engaging in global cooperation to advance AI technologies effectively.
Technological Competitiveness
Competing with global tech giants requires cutting-edge AI models and infrastructure. While building foundational models from scratch may be impractical for most organizations, leveraging open-source models and fine-tuning them with local data offers a cost-effective path to competitiveness.
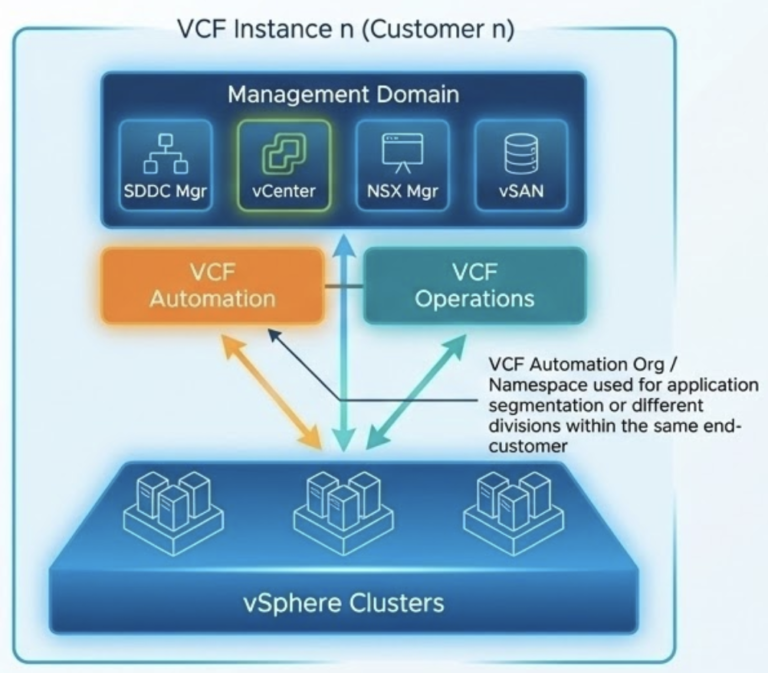
Scalable Infrastructure for Sovereign AI
Private AI Infrastructure
VMware Private AI Foundation with NVIDIA provides a secure, on-premises AI infrastructure tailored for EU member states and other regions pursuing AI sovereignty. This platform integrates scalable NVIDIA hardware and open-source tools, enabling organizations to:
– Virtualize and optimize AI workloads.
– Reduce energy consumption and total cost of ownership.
– Avoid vendor lock-in through open APIs and Kubernetes integration.
– Access open-source AI models via repositories like Hugging Face.
Optimized Hardware Solutions
Broadcom enhances sovereign AI infrastructure with high-performance networking and storage technologies. Their Ethernet-based switches and NICs offer ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, ensuring efficient data flow for AI training and inference. Broadcom’s commitment to open standards supports flexibility and avoids proprietary lock-in.
Ensuring Data Sovereignty and Security
On-P